



Next: Amplification
Up: Tensor Products
Previous: Some formulae for the
Contents
Index
In
the case of bilinear mappings between operator spaces
one has to distinguish between two different notions of
complete boundedness:
on one hand we have the jointly completely bounded
[BP91, Def. 5.3 (jointly completely bounded)]
and, on the other hand, the completely bounded bilinear
mappings
[CS87, Def. 1.1].
The class of completely bounded bilinear maps is
is contained in the first one.
These notions are in perfect analogy to those of bounded bilinear forms on normed spaces.
For completely bounded bilinear mappings, we have at our disposal similar
representation
and
extension theorems47
as in the case of completely bounded linear maps.
There are two tensor products corresponding to the above two classes of bilinear mappings,
namely the projective
and the
Haagerup tensor product.
Depending on the class of bilinear maps, one uses different methods to define
the
amplification
of a bilinear mapping
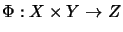 .
.
Footnotes
- ... theorems47
- Extension theorems for
completely bounded bilinear (and, more generally, multilinear) maps
can be derived from the injectivity of the
Haagerup tensor product .
Subsections




Next: Amplification
Up: Tensor Products
Previous: Some formulae for the
Contents
Index
Prof. Gerd Wittstock
2001-01-07