



Next: The dual
Up: Operator Spaces and Completely
Previous: Columns and rows of
Contents
Index
Let 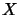 and
and 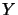 be matricially normed spaces.
A matrix
be matricially normed spaces.
A matrix
![$ [T_{ij}]\in M_n(\mathit{CB}(X,Y))$](img121.png) determines a completely bounded operator
determines a completely bounded operator
Defining
![$ \left\Vert\left[T_{ij}\right]\right\Vert=\Vert T\Vert _\mathrm{cb}$](img125.png) ,
,
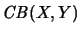 becomes
a matricially normed space .
It is an operator space , if
becomes
a matricially normed space .
It is an operator space , if 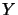 is one.
The equation
holds completely isometrically.
is one.
The equation
holds completely isometrically.
Prof. Gerd Wittstock
2001-01-07