



Next: Column Hilbert space factorization
Up: The column Hilbert space
Previous: Tensor products
Contents
Index
In connection with the
column Hilbert space , it is enough
to calculate the
row norm
or the
column norm
of an operator 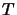 , instead of the
, instead of the
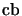 -norm, to ascertain the complete boundedness.
-norm, to ascertain the complete boundedness.
Let 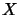 be an operator space and
be an operator space and
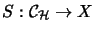 bzw.
bzw.
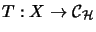 .
Then we have
.
Then we have
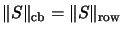 resp.
resp.
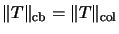 ([Mat94, Prop. 4]
resp. [Mat94, Prop. 2]).
([Mat94, Prop. 4]
resp. [Mat94, Prop. 2]).
The column Hilbert space is characterized as follows,
- (A)
- as a hilbertian operator space
[Mat94, Thm. 8]:
For an operator space 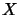 on an Hilbert space
on an Hilbert space 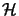 , we have
the following equivalences:
, we have
the following equivalences:
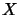 is completely isometric to
is completely isometric to
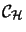 .
.
- For all operator spaces
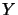 and all
and all
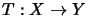 we have
we have
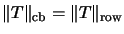 ,
and for all
,
and for all
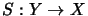 we have
we have
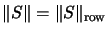 .
For all operator spaces
.
For all operator spaces 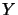 and all
and all
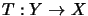 we have
we have
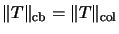 ,
and for all
,
and for all
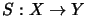 we have
we have
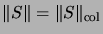 .
.
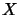 coincides with the
maximal hilbertian operator space
on columns and with the
minimal hilbertian operator space
on rows. That means isometrically
coincides with the
maximal hilbertian operator space
on columns and with the
minimal hilbertian operator space
on rows. That means isometrically
- (B)
- as an operator space:
For an operator space
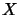 TFAE:
TFAE:
- There is a Hilbert space
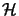 , such that
, such that
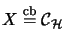 completely isometrically.
completely isometrically.
- We have
and
isometrically.
[Mat94, Thm. 10].
-
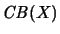 with the composition as multiplication
is an operator algebra
[Ble95, Thm. 3.4].
with the composition as multiplication
is an operator algebra
[Ble95, Thm. 3.4].




Next: Column Hilbert space factorization
Up: The column Hilbert space
Previous: Tensor products
Contents
Index
Prof. Gerd Wittstock
2001-01-07
![$\displaystyle \Vert T\Vert _{\mathrm{row}}
:=\sup_{n \in {\mathbb{N}}}
\sup_{\...
...}(X)}\leq 1}
\left\Vert\left[Tx_1 \ldots Tx_n\right]\right\Vert _{M_{1,n}(Y)}
$](img404.png)
![$\displaystyle \Vert T\Vert _{\mathrm{row}}
:=\sup_{n \in {\mathbb{N}}}
\sup_{\...
...}(X)}\leq 1}
\left\Vert\left[Tx_1 \ldots Tx_n\right]\right\Vert _{M_{1,n}(Y)}
$](img404.png)
![$\displaystyle \Vert T\Vert _{\mathrm{col}}
:=\sup_{n \in {\mathbb{N}}}
\sup_{\...
...rray}{c}Tx_1\\ \vdots \\ Tx_n \end{array}
\right]\right\Vert _{M_{n,1}(X)}
$](img405.png)
![]() be an operator space and
be an operator space and
![]() bzw.
bzw.
![]() .
Then we have
.
Then we have
![]() resp.
resp.
![]() ([Mat94, Prop. 4]
resp. [Mat94, Prop. 2]).
([Mat94, Prop. 4]
resp. [Mat94, Prop. 2]).
![]() on an Hilbert space
on an Hilbert space ![]() , we have
the following equivalences:
, we have
the following equivalences:
![]() is completely isometric to
is completely isometric to
![]() .
.
![]() and all
and all
![]() we have
we have
![]() ,
and for all
,
and for all
![]() we have
we have
![]() .
For all operator spaces
.
For all operator spaces ![]() and all
and all
![]() we have
we have
![]() ,
and for all
,
and for all
![]() we have
we have
![]() .
.
![]() coincides with the
maximal hilbertian operator space
on columns and with the
minimal hilbertian operator space
on rows. That means isometrically
coincides with the
maximal hilbertian operator space
on columns and with the
minimal hilbertian operator space
on rows. That means isometrically
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()