



Next: Joint amplification of a
Up: Tensor products
Previous: Tensor products
Contents
Index
Tensor products of operator matrices
As usual we define the algebraic tensor product of operator matrices
![$ x = [x_{ij}] \in M_{p}(X)$](img887.png) ,
,
![$ y = [y_{kl}] \in M_{q}(Y)$](img888.png) by setting
Here we have used the definition
by setting
Here we have used the definition
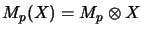 and the associative law
and the associative law
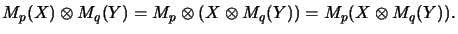 |
(5) |
In view of the next identification one should note that the
shuffle-map is an algebraic isomorphism:
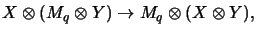 |
(6) |
for
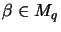 ,
, 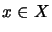 ,
, 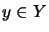 .
The shuffle-isomorphism at hand we obtain the identification:
Finally we use the usual72
identification
.
The shuffle-isomorphism at hand we obtain the identification:
Finally we use the usual72
identification
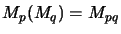 to obtain
to obtain
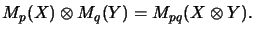 |
(7) |
We call this algebraic isomorphism the
shuffle-isomorphism.
One should note that for operator space tensor products
the algebraic identifications
(![[*]](crossref.png) ) and (
) and (![[*]](crossref.png) )
are only complete contractions:
)
are only complete contractions:
In general these are not isometries even for 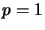 resp.
resp. 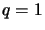 .
For an operator space tensor product the
shuffle-map
.
For an operator space tensor product the
shuffle-map
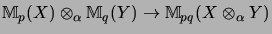 |
(10) |
in general is
only
completely contractive.
In the case of the
injective operator space tensor product
this is of course a complete isometry.
More generally, one considers the shuffle-map for
rectangular matrices73:
Another example is provided by the Blecher-Paulsen
equation .
Footnotes
- ... usual72
- In the matrix so obtained
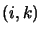 are the row indices and
are the row indices and 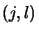 are the
column indices, where
are the
column indices, where
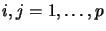 and
and
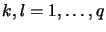 .
The indices
.
The indices 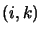 resp.
resp. 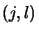 are ordered lexicographically.
are ordered lexicographically.
- ... matrices73
- The shuffle-map
 ,
, ,
,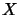 ,
,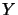 operator spaces, has been studied for various combinations of
operator space tensor products
[EKR93, Chap. 4].
operator spaces, has been studied for various combinations of
operator space tensor products
[EKR93, Chap. 4].




Next: Joint amplification of a
Up: Tensor products
Previous: Tensor products
Contents
Index
Prof. Gerd Wittstock
2001-01-07
![[*]](crossref.png) ) and (
) and (![[*]](crossref.png) )
are only complete contractions:
)
are only complete contractions: