



Next: Columns and rows of
Up: Elementary constructions
Previous: Subspaces and quotients
Contents
Index
Matrices over an operator space
The vector space 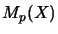 of
matrices over a matricially normed space
of
matrices over a matricially normed space 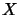 itself is matricially
normed in a natural manner: The norm on the
itself is matricially
normed in a natural manner: The norm on the 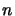 th level
th level
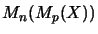 is given by the identification
[BP91, p. 265].
We8write
for
is given by the identification
[BP91, p. 265].
We8write
for 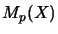 with this operator space structure.
In particular,
holds isometrically.
Analogously
with this operator space structure.
In particular,
holds isometrically.
Analogously
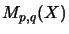 becomes a matricially normed space
becomes a matricially normed space
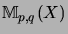 by the identification
by the identification
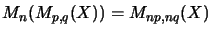
.
By adding zeros it is a subspace of
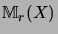 for
for
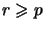 ,
, 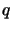 .
.
Examples:
For a 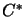 -algebra
-algebra 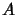 ,
,
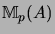 is the
is the 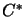 -Algebra of
-Algebra of 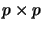 -matrices over
-matrices over 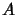 with its
natural operator space structure.
with its
natural operator space structure.
The Banach space 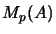 is the first matrix level of the
operator space
is the first matrix level of the
operator space
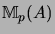 .
.
The complex numbers have a unique operator space structure which on the first
matrix level is isometric to
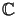 , and for this
, and for this
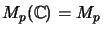 holds isometrically.
We write
holds isometrically.
We write
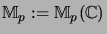
.
Then
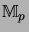 always stands for the
always stands for the 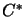 -algebra of
-algebra of
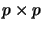 -matrices with its
operator space structure. The Banach space
-matrices with its
operator space structure. The Banach space 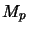 is the first matrix level
of the operator space
is the first matrix level
of the operator space
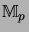 .
.
Footnotes
- ...
We8
-
In the literature, the symbol
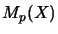 stands for both the operator space with first
matrix level
stands for both the operator space with first
matrix level 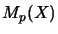 and for the
and for the 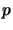 th level of the operator space
th level of the operator space 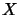 .
We found that the distinction between
.
We found that the distinction between
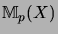 and
and 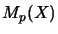 clarifies for instance the definition of the operator space
structure of
clarifies for instance the definition of the operator space
structure of 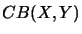 .
.




Next: Columns and rows of
Up: Elementary constructions
Previous: Subspaces and quotients
Contents
Index
Prof. Gerd Wittstock
2001-01-07
![]() -algebra
-algebra ![]() ,
,
![]() is the
is the ![]() -Algebra of
-Algebra of ![]() -matrices over
-matrices over ![]() with its
natural operator space structure.
with its
natural operator space structure.
![]() is the first matrix level of the
operator space
is the first matrix level of the
operator space
![]() .
.
![]() , and for this
, and for this
![]() holds isometrically.
We write
holds isometrically.
We write