



Next: Construction of :
Up: Operator Spaces and Completely
Previous: -direct sums
Contents
Index
Let 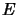 be a normed space. Among all operator space norms on
be a normed space. Among all operator space norms on
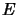 which coincide on the first matrix level with the given
norm, there is a greatest and a smallest. The matricially normed spaces given by these
are called
which coincide on the first matrix level with the given
norm, there is a greatest and a smallest. The matricially normed spaces given by these
are called
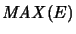 and
and
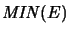 . They are characterized by the following
universal mapping property:14
For a matricially normed space
. They are characterized by the following
universal mapping property:14
For a matricially normed space 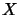 ,
,
and
holds isometrically.
We have [Ble92a]
For
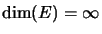 ,
,
is not completely bounded[Pau92, Cor. 2.13].15
Subspaces of
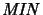 -spaces are
-spaces are
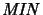 -spaces: For each isometric mapping
-spaces: For each isometric mapping
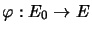 , the mapping
, the mapping
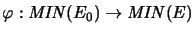 is completely isometric.
is completely isometric.
Quotients of
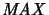 -spaces are
-spaces are
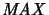 -spaces: For each quotient mapping
-spaces: For each quotient mapping
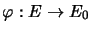 , the mapping
, the mapping
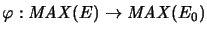 is a complete quotient mapping.
is a complete quotient mapping.
Footnotes
- ... property:14
-
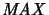 is the left adjoint and
is the left adjoint and
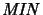 the right adjoint of the forgetfull functor which
maps an operator space
the right adjoint of the forgetfull functor which
maps an operator space 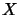 to the Banach space
to the Banach space 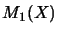 .
.
- ...Paulsen92.15
-
Paulsen uses in his proof a false estimation for the projection constant of the finite
dimensional Hilbert spaces; the converse estimation is correct
[Woj91, p. 120], but here useless.
The gap can be filled [Lam97, Thm. 2.2.15]
using the famous theorem of Kadets-Snobar:
The projection constant of an
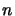 -dimensional Banach space is less or equal
than
-dimensional Banach space is less or equal
than 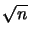 [KS71].
[KS71].
Subsections




Next: Construction of :
Up: Operator Spaces and Completely
Previous: -direct sums
Contents
Index
Prof. Gerd Wittstock
2001-01-07
![]() be a normed space. Among all operator space norms on
be a normed space. Among all operator space norms on
![]() which coincide on the first matrix level with the given
norm, there is a greatest and a smallest. The matricially normed spaces given by these
are called
which coincide on the first matrix level with the given
norm, there is a greatest and a smallest. The matricially normed spaces given by these
are called
![]() and
and
![]() . They are characterized by the following
universal mapping property:14
For a matricially normed space
. They are characterized by the following
universal mapping property:14
For a matricially normed space ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() -spaces are
-spaces are
![]() -spaces: For each isometric mapping
-spaces: For each isometric mapping
![]() , the mapping
, the mapping
![]() is completely isometric.
is completely isometric.
![]() -spaces are
-spaces are
![]() -spaces: For each quotient mapping
-spaces: For each quotient mapping
![]() , the mapping
, the mapping
![]() is a complete quotient mapping.
is a complete quotient mapping.